

National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA), Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) have all set standards on hazardous occupational noise in their respective industries. If you feel like you may be at risk for hazardous noise exposure or want to learn more, contact The Hearing Doctor to schedule an appointment with one of our providers.In the USA, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) work together to provide standards and regulations for noise in the workplace. Occupational stress can cause more health and safety risks due to attention and irritability. Occupational stress – Persistent exposure to loud sounds while working can induce stress to the worker, even at low levels of noise.Tinnitus is the medical term for the sensation of hearing a ringing or buzzing sound.

Tinnitus – Ringing in the ears is an early sign of damage to your ears.Hazardous levels of noise vary based on the amount in dB and length of exposure time. Noise-induced hearing loss – This is the most common effect of exposure to hazardous noise and is listed as the most common preventable health condition.Effects of Hazardous Noise in the Workplace
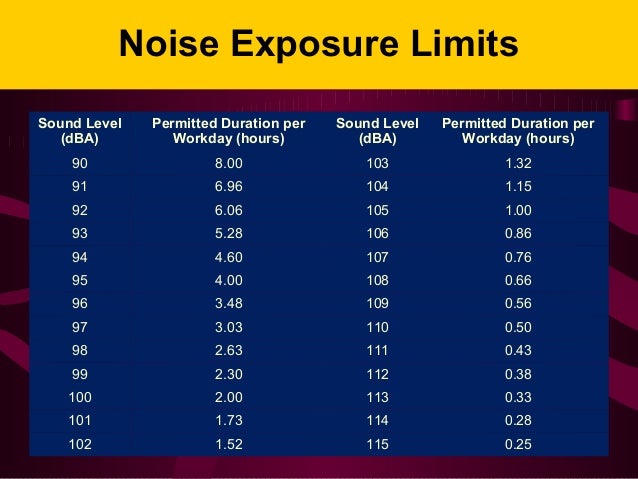
Both types of noise exposure can cause permanent damage without appropriate use of hearing protection. It is important to note that both types of hazardous noise may appear to be “safe,” as one doesn’t last very long and the other is a more tolerable level of noise. However, if you are around this type of noise daily, it can begin to affect your ability to hear long-term. For example, construction noise may not always be extremely loud. The noise levels may be more tolerable but have been shown to cause significant damage over time. Prolonged hazardous noise exposure is usually lower in dB level but can cause permanent hearing damage. An example of a source that can generate sudden bursts of noise would be a machine press. Sudden noises can easily reach over 120dB, which can cause permanent hearing damage after only a few seconds. People are often not prepared ahead of time when these noises occur and may not have hearing protection nearby. Sudden bursts of extremely loud noise can cause immediate damage to your ears. There are two types of risks related to hazardous noise. For example, if the noise level increases to 90 dB, the exposure time should not exceed 6 hours. The rule of thumb is for every 5 dB increase in noise level, the exposure time should be reduced by 50%. At this level of exposure, all employees exposed are required to have access to feasible hearing protection. At What Decibel Is Hearing Protection Required?Īccording to the Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA), “hazardous” noise is defined as exposure to 85dB or more lasting an 8-hour working period. Regardless of your job title or workplace environment, it is important to be familiar with hearing health recommendations and when to use hearing protection. Other types of hearing health and safety risks can include rupture of the eardrums and ringing in the ears. Employment in an environment with daily/occasional exposure to hazardous noise poses many health and safety risks, including the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Hazardous noise levels have been identified in many workplace environments, which can cause permanent or temporary damage to the organ for hearing.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
